기계학습 모델을 활용한 공장지붕형 태양광 구조물의 안전성 평가
Copyright © 2024 by Korean Society of Steel Construction
초록
태양광 발전설비 설치 시 비전문가들의 초기 설계와 태양광 구조검토 시 반복적인 설계변경으로 인해 생기는 시간 비용을 해결하기 위한 기계학습 모델을 제안한다. 기계학습 모델로는 K최근접이웃(K-Nearest Neighbors)과 로지스틱회귀(Logistic Regression)를 적용하였다. 최적의 하이퍼 파라미터를 탐색하기 위하여 그리드서치(Grid Search)를 사용했다. 표준화 변환(Standard Scaler)을 사용하여 모델의 성능을 높였다. F1스코어(F1-score)를 사용하여 모델을 평가했다. 2가지 모델은 80 % 이상의 정확도를 보여주었지만, 안전 클래스에 대한 정확도가 낮았다. 2가지 클래스의 불균형으로 인한 데이터 편향이 생긴 것으로 예상된다. 데이터 세트의 조정 및 전처리, 다른 기계학습 모델의 사용을 통해 데이터 편향에 대한 추가적인 연구가 필요하다.
Abstract
This paper proposes a machine learning model to address the time and cost inefficiencies caused by the initial designs of non-experts and repeated design changes during the structural design of photovoltaic installations. The study applies K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) and Logistic Regression as the machine learning models. GridSearch was used to find the optimal hyperparameters, while StandardScaler was employed to improve model performance. The F1-score was utilized to evaluate the performance of the models. Both models demonstrated a low prediction accuracy for the safety class, likely due to data bias caused by class imbalance. Further research is needed to mitigate this data bias through dataset adjustment and preprocessing, and the exploration of alternative machine learning models.
Keywords:
Steel structures, Solar structures, Machine learning, KNN, Logistic Regression키워드:
강구조, 태양광구조물, 머신러닝, K최근접이웃, 로지스틱 회귀1. 서 론
최근 신재생 에너지에 대한 관심이 높아짐에 따라, 태양광 발전소에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있는 추세이다[1]. 특히, 건축물 지붕 상부에 설치되는 태양광의 경우 정부의 지원과 세제 혜택 등으로 설치가 증가하고 있다. 일반적으로 건축물 상부 태양광 설계는 태양광 구조물 계획, 태양광 구조물 안전성 검토, 태양광 구조물에 따른 건축물의 안전성 검토, 필요 시 건축물 보강안 검토 또는 태양광 구조물 재설계를 통한 안전성 확보 등의 순환적인 설계과정을 거치고 있다. 태양광 구조물 계획단계에서는 일반적으로 구조 전문가가 아닌 비전문가 경험에 따라 초기 설계를 진행한다. 이후 초기 설계안을 토대로 공사비용을 산정하여 계약 후 구조업체에서 구조해석을 진행하게 된다. 이로 인해, 초기 계약 단계에서는 전문적인 구조해석이 제외된다.
태양광 구조물 설계과정은 모듈 하부 중도리 설계, 보와 기둥 설계, 접합부 설계의 과정으로 진행된다. 그러나 사업 타당성을 평가하기 위한 초기 설계는 일반적으로 비전문가의 경험과 현장 상황에 맞춘 설계가 이루어짐에 따라, 구조안전성을 만족하지 못하는 경우가 많다. 그로 인해 실시 설계 단계에서 시공자와 구조검토를 진행하는 전문가 간의 반복적인 설계 협의와 재검토로 인하여, 많은 인력과 시간 비용이 소요되는 어려움이 있다. 초기 설계 시 예상된 공사비용 부분에서도 설계변경에 따른 재계약 등의 문제가 발생한다.
최근 인공지능 및 기계학습의 발전으로 건축에서도 이를 활용하는 연구들이 많이 증가하고 있다[2]. Baduge[3]에서 건축 설계 분야에서 사용되는 기계학습과 인공지능 방법에 대해 설명하고 있다. 건축구조 분야에서도 기계학습을 이용하여 반복적인 과정에 대한 시간 단축과 최적화 설계를 위하여 많이 활용하고 있다. 강구조물의 최적 설계와 트러스의 단면 및 형상 최적 설계에 대하여 Kim[4],[5]에서 연구되었다. Hashemi[6]에선 MRF철골 구조물의 상세 설계 전 중량 예측 모델에 대해서 연구되었다. Gupta[7]는 KNN 모델을 활용하여 강철 미세구조 유형의 다중 클래스 분류 모델을 제안하고 F1스코어를 통해 평가하였다. Lee[8]는 CFST 기둥의 공칭강도를 예측하는 기계학습 모델을 제안하였으며, Ha[9]는 교량의 백아화 등급을 정량적으로 평가하며, 평가 과정의 간소화를 위한 기계학습 기법을 연구하였다. Duong[10]은 축방향 하중을 받는 다양한 단면의 CFST 기둥에 대한 기계학습 모델을 제안하였다. Jang[11]과 Kim[12]에선 다양한 기계학습 모델들이 콘크리트의 균열 깊이를 예측하는 성능을 평가하였으며, Jeong[13]은 콘크리트 균열의 용접 결함을 평가하는 기계학습 모델을 제안하였다.
본 연구에서는 건축물 지붕 태양광 구조물 설계과정에서 기계학습 모델을 하고자 하며, 초기 설계 단계에서 태양광 구조물의 안전성에 대한 정확한 평가를 제공할 수 있는 의사결정 모델을 만들고자 한다.
2. 설계 개요
2.1 태양광 구조물 개요
건축물 위 태양광 구조물 설계는 모듈을 지지하는 중도리 설계, 중도리를 지지하는 보와 기둥 설계, 가새 및 하부 건축물과의 접합부 설계, 건축물의 안전성 검토 순으로 진행된다. 중도리, 보 및 기둥은 태양광 설치 공사 시 모듈을 제외하고, 가장 많은 부분을 차지하고 있다. 중도리의 경우 C형강을 사용하며, 보와 기둥의 경우 각형강관을 사용한다. 구조물의 안전성은 부재의 성능을 높이기보다는, 설치 간격의 변경을 통해 확보한다. 가새 및 접합부 설계는 건축물의 지붕 형태, 접합 위치, 볼트의 종류 등 고려할 변수가 다양하며, 시공사마다 다양한 방식을 사용하고 있다. 하부 건축물 안전성의 경우에는 건축물의 보수ㆍ보강보다는 태양광 구조물의 재설계를 통하여 만족시킨다. 이는 기존에 사용 중인 건축물의 보수ㆍ보강의 한계와 비용의 문제가 원인이다. 본 연구에서는 태양광 설계과정 속에서 반복적인 설계와 시공자와의 많은 협의가 필요하며, 초기 설계 시 중요한 중도리 및 보, 기둥 설계에 중점을 두고 연구를 진행하였다. 건축물의 보수ㆍ보강은 비전문가가 현장에서 구조검토에 필요한 조건을 파악하기에 어려움이 있다. 따라서 건축물의 보수ㆍ보강 유무의 판단은 제외되었다.
2.2 설계 조건 및 고려 사항
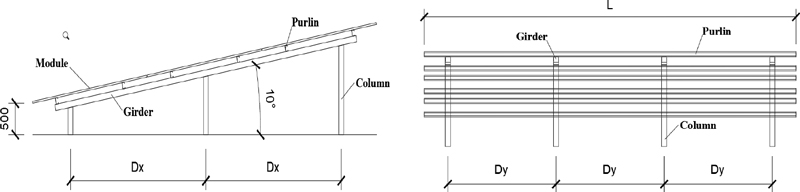
본 연구에서는 태양광 구조물을 대상으로 평가모델을 개발하였다. 태양광 구조물은 건축물 지붕으로부터 500 mm 이격되어 설치된다. 500 mm는 태양광 설치 이후 점검 및 보수를 위하여 일반적으로 설계되는 높이다. 모듈의 설치 각도는 건축물의 대지 조건, 발전 용량에 중점을 두고 결정되는 요소로, 본 연구에서는 10°를 적용하였다. 태양광 모듈은 3장씩 나열되어 설치되는 3V 구조물로 설계하였다.
태양광 구조물의 경우 고정하중, 설하중 및 풍하중에 대하여 구조해석을 수행한다. 일반적으로 고정하중, 설하중보다는 풍하중이 안전성에 지배적인 영향을 준다. 고정하중은 모듈 및 부수적인 전기 설비들로 일반적으로 1m2당 0.2 kN – 0.25 kN으로 산정된다. 본 연구에서 고정하중은 0.25 kN을 적용하였고, 설하중의 경우 통상적인 국내 건축구조 설계 조건인 0.5 kN/m2를 사용하였다. 풍하중의 산정 조건은 대부분 기계학습의 변수로 사용된다. 다만, 지표면 조도의 경우 국내 내륙지방의 조건인 C에 대한 해석 결과들이 사용되었다.
구조물의 부재로는 중도리 단면이 C-100 × 50 × 20 × 2.3이고, 보와 기둥은 각형강관 □-100 × 100 × 2.3 t로 설계되었다. 각 부재의 강종은 SRT275를 기준으로 진행되었다. 구조물의 중도리와 보, 기둥은 완전 일체화로 가정되었으며, 기둥의 하부는 고정단으로 설계된다.
2.3 데이터 베이스
기계학습 모델에 사용된 데이터베이스는 국가건설기준(KDS)의 건축구조기준 설계하중(KDS 41 10 15 : 2019)[14]과 건축물 강구조 설계기준(KDS 41 30 10 : 2019)[15]을 토대로 MIDAS 해석 결과를 취합하였다.
데이터는 3,061개가 사용되었다. 구조안전성을 만족하는 클래스 512개와 안전성을 만족하지 못하는 클래스 2,549개로 구성되었다. 불안전 클래스는 풍속(Vo), 보 간격(Dy), 기둥 간격(Dx), 건축물 높이(H)로 인하여 안전성을 만족하지 못하는 경우이다. 각각의 클래스 수는 Table 1에서 확인할 수 있다. 기계학습 모델링의 편의성을 위하여 안전 클래스는 ‘1’, 불안전 클래스는 ‘0’으로 기계학습에 적용하였다.
기계학습 모델의 입력변수로는 Vo, Dx, Dy, H에 중도리 길이(L)가 추가된 총 5가지이다. 각 변수들은 Fig. 1에서 확인이 가능하다. 풍속의 경우 24 m/s에서 38 m/s로 국내의 풍속 기준을 가지고 있다. 보 간격의 경우에는 최소 1.6 m에서 최대 3.7 m사이의 범위에, 기둥 간격은 최소 2.6 m, 최대 3.0 m의 범위 내에서 다양하게 분포되어 있다. 건축물 높이는 5 m부터 20 m 범위에 있고, 중도리의 길이는 모듈 6장, 10장, 14장, 18장 4가지 경우에 대하여 사용된다. 데이터들은 훈련 세트 70 %, 테스트 세트 30 %의 비율로 기계학습 모델의 학습 및 평가에 사용된다.
3. 기계학습 모델
3.1 KNN
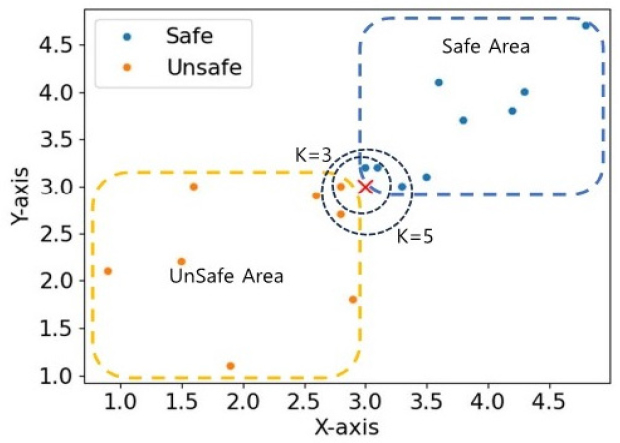
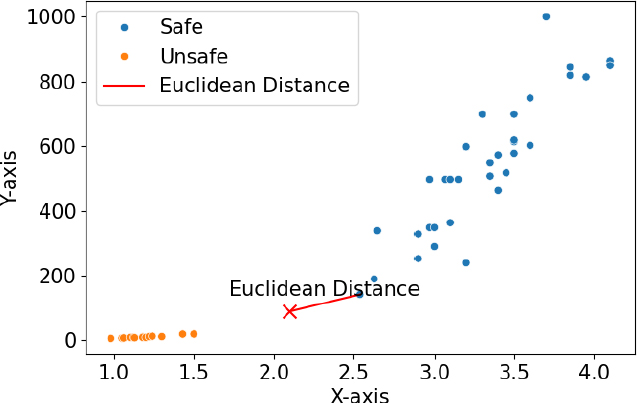
KNN 알고리즘은 이웃 알고리즘 지도 학습이다. 새로운 변수를 제공했을 때 학습된 데이터와 가까운 K개의 이웃 데이터를 선택한다(Fig. 2). 학습된 데이터를 통해 안전 클래스와 불안전 클래스가 분포된다. 새로운 데이터를 입력하면 가까운 K개의 데이터를 선택하여 예측을 진행한다. K개의 데이터는 각 데이터 간의 거리인 유클리드 거리를 기준으로 선택하게 된다(Fig. 3). 선택된 데이터들의 다수결의 원칙을 통하여 최종적인 예측을 진행한다. 이로 인해, KNN 모델은 예측 시 가정이 포함되지 않는다. 회귀 문제 적용 시에도 동일한 과정을 통해 평균값을 구하여 예측이 가능한 알고리즘이다. 모델의 구성은 변수의 종류만큼 차원을 구성하게 된다. 변수 차원의 경계가 확실한 경우 모델의 성능이 뛰어나다. 반대로 데이터의 패턴이 복잡해 경계의 구분이 어려운 경우 모델의 성능이 저하된다. 분류 문제에서 클래스의 양이 일정하지 않으면 적은 데이터 클래스에 대한 예측 성능이 떨어질 수 있다. 이때에는 과표본화(over sampling), 하표본화(down sampling) 등 다양한 데이터 전처리를 통해 모델의 성능을 높이는 과정이 필요하다.
3.2 Logistic Regression
로지스틱 회귀 알고리즘은 명칭은 회귀이지만 분류모델에 속한다. 선형 회귀와 동일하게 선형방정식을 통해 모델이 학습하게 된다. 식으로 표현하면 다음과 같다.
| (1) |
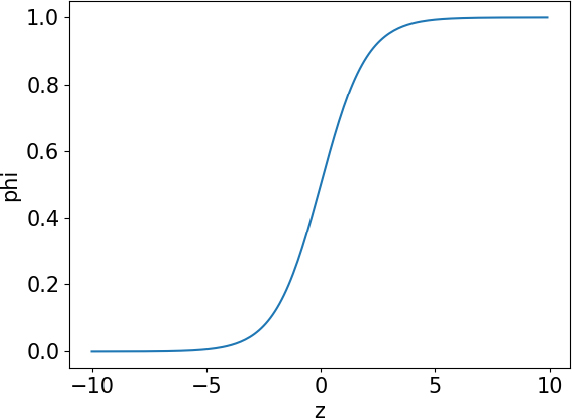
여기서 a, b, c, d, e는 각 변수에 대한 가중치 또는 계수이다. z가 0–1사이의 값이 되어야 확률이 된다. 이를 위해 시그모이드 함수가 사용된다. 시그모이드 함수는 아래 식과 같다.
| (2) |
선형방정식에서 얻은 z의 모든 값을 0–1 범위 내의 수로 만들어 확률로 예측이 가능하다. 시그모이드 함수를 그래프로 표현하면 Fig. 4와 같다.
3.3 그리드서치(GridSearch)
기계학습에는 하이퍼 파라미터라는 요소가 고려된다. 하이퍼 파라미터란 모델의 학습 과정을 조절하는 요소이다. 기계학습 모델의 학습 횟수, 탐색 방법 등 모델의 예측 성능에 결정적인 요소이다. Thai[16]의 연구에서 향후 건축구조 분야에 기계학습 모델의 적용 시 하이퍼 파라미터에 대한 중요성을 설명하고 있다.
KNN 모델의 하이퍼 파라미터로는 K(n_neighbors), 거리 측정 방법(metric), 가중치(weights)의 3가지가 존재한다. K는 이웃한 몇 개의 데이터를 선택하여 예측을 진행할지 결정한다. K는 값에 따라 모델의 성능이 달라지는 중요한 하이퍼 파라미터이며, 다수결의 원칙에서 동률이 나오는 것을 방지하기 위하여 홀수로 설정한다. 거리 측정 방법은 유클리드 거리와 맨해튼 거리 중 선택하도록 하였다. 유클리드 거리는 두 점 사이의 직선 거리이고, 맨해튼 거리는 직각 거리이다. 가중치에는 uniform, distance의 2가지가 있다. uniform은 모든 이웃에 동일한 가중치를 부여하는 방법이고, distance는 거리가 가까운 이웃일수록 더 큰 가중치를 부여하는 방법이다.
로지스틱 회귀 모델의 하이퍼 파리미터는 C, 규제 방식(Penalty), 최적화 알고리즘(Solver), 학습횟수(Max-iter)가 있다. C는 L1, L2 규제에 곱해지는 상수로, 강도를 조절한다. C값이 커질수록 규제가 약해져서 과적합이 일어날 위험이 있다. C값이 작아질수록 규제가 강해져 모델이 단순하지만, 그로 인해 과소 적합이 생길 수 있다. 규제 방식은 L1과 L2가 있다. L1은 모델의 계수에 대한 절대값의 합을 최소화한다. 일부 특징의 가중치를 0으로 만들어 특징 선택(feature selection) 효과를 얻을 수 있다. L2는 모든 변수의 가중치를 작게 만들어 과대 적합을 방지한다. 최적화 알고리즘은 Liblinear와 Sag가 있다. Liblinear은 소규모 데이터 세트나 L1 규제 시 사용된다. Sag는 L1과 L2를 모두 지원하며, 데이터 세트의 크기가 대규모일 때 사용된다.
그리드 서치(GridSearch)는 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝 방법이다. 하이퍼 파라미터들을 격자처럼 엮어서 모든 조합을 시도하여 학습된 모델에 최적의 성능을 보여주는 하이퍼 파라미터를 찾아주는 역할을 한다. 모델을 찾는 과정이 직관적이고 최적의 값을 찾을 확률이 높지만, 하이퍼 파라미터의 종류나 조합이 다양할 경우 오랜 시간이 걸릴 수 있는 단점이 있다.
3.4 결과
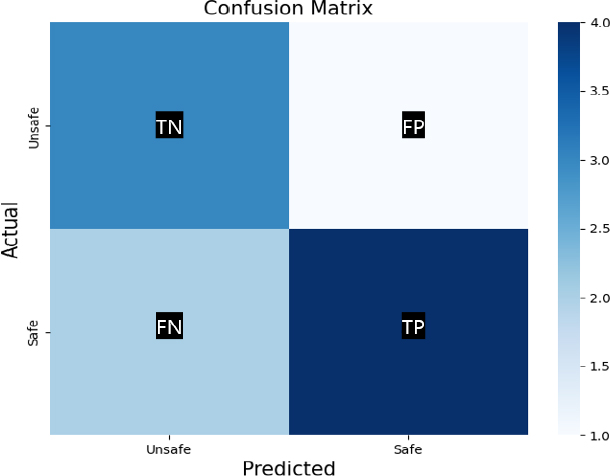
기계학습 모델을 평가하기 위해 F1스코어(F1-score)를 사용하였다. F1스코어란 정밀도(Precision)와 재현율(Recall) 값을 구하여, 모델의 오차를 나타내는 혼동행렬이다(Fig. 5). 정밀도란 모델이 양성으로 예측한 것 중 실제로 양성인 비율로, 모델이 얼마나 정확히 양성 클래스를 예측하는 지를 나타낸다. 재현율이란 양성인 것 중 모델이 양성으로 예측한 비율로, 모델이 얼마나 많은 양성 클래스를 찾아내는 지를 나타낸다. F1스코어는 정밀도와 재현율의 조화 평균이다.
실제 데이터에서 한쪽 클래스의 비율이 높을 경우, 모델이 데이터가 많은 클래스에 대한 예측 정확도가 높아서 전체 정확도가 높게 나올 수 있다. 정확도는 높지만 실제로는 유용하지 않은 모델이 만들어지는 것이다. 이를 방지하기 위하여 F1스코어를 통한 평가가 필요하다. F1스코어는 이진 분류 문제에 사용되며, 다중 분류 문제시에는 마이크로 평균 F1스코어, 매크로 평균 F1스코어 등 다른 평가지표를 사용해야 한다. 본 연구는 이진 분류 문제에 속하기 때문에 F1스코어를 사용하였다. F1스코어의 산정방법은 아래와 같다. TP는 양성을 양성으로 예측한 경우, TN은 음성을 음성으로 예측한 경우이다. FP와 FN은 예측을 반대로 한 경우이다.
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
각 모델에 대하여 그리드 서치에 의해 탐색된 최적의 하이퍼 파라미터를 Table 2에서 확인할 수 있다. Table 3는 각 모델의 정밀도, 재현율, F1스코어에 대한 결과를 보여주고 있다.
KNN 모델의 F1스코어는 불안전 클래스에 대해서는 훈련 세트 0.90, 테스트 세트 0.89로 좋은 성능을 보여주었다. 그러나 안전 클래스에서는 예측을 하지 못하였다. 변수 크기 차이에 따른 유클리드 거리의 오류 또는 안전 클래스와 불안전 클래스의 데이터 개수 차이로 인한 데이터 편향이 일어난 것으로 판단된다.
로지스틱 회귀 모델의 F1스코어는 안전 클래스에 대해서는 훈련 세트 0.51, 테스트 세트 0.62, 불안전 클래스에 대해서는 훈련 세트 0.92, 테스트 세트 0.93으로 불안전 클래스에서 좋은 성능을 보여주었다. 훈련 세트보다 테스트 세트의 점수가 더 높기에 보완이 필요할 것으로 판단된다. 학습 횟수는 10000으로 예측 시간이 다소 오랜 시간이 소요되었다.
3.5 정확도 향상 기법
변수의 크기 차이로 인한 유클리드 거리의 오류를 해결하기 위하여 스케일링 기법 중 표준화 변환기(StandardScaler)를 사용하였다. 표준화 변환기란 변수 데이터들을 같은 스케일로 맞춰주는 역할을 한다. 식으로 표현하면 아래와 같다.
| (6) |
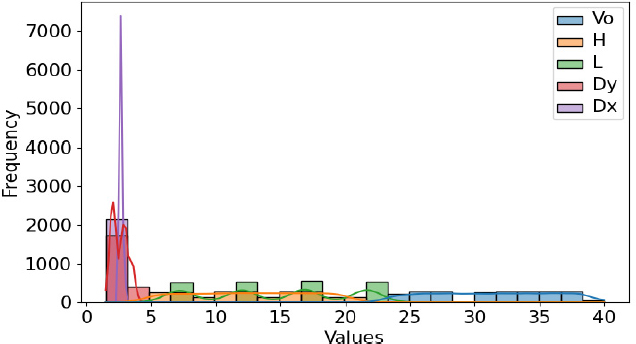
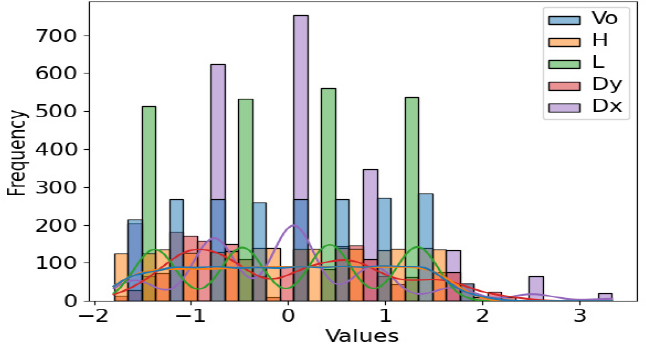
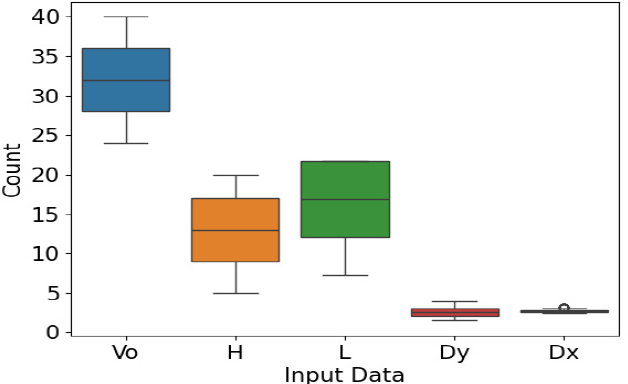
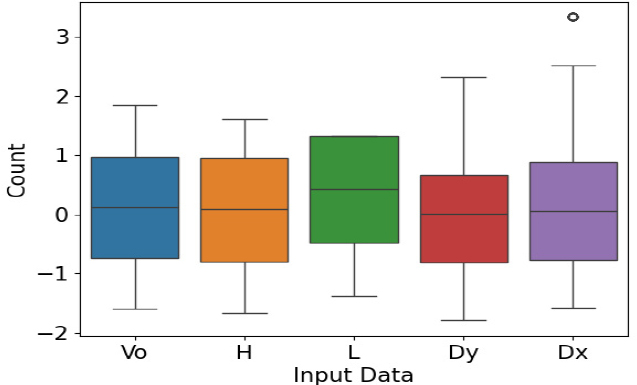
x는 변수값, μ는 변수값들의 평균(mean), σ는 변수들의 표준편차(standard deviation)이다. 표준화 변환 전과 후의 데이터들의 크기 및 분포를 확인하였고, Fig. 6는 이를 히스토그램으로 나타낸 것이다. Fig. 6에서 막대그래프를 통해 데이터들이 각 스케일에 맞게 위치하는 것을 확인하였다. 물결선은 데이터가 분포되어 있는 정도로, 보 간격과 기둥 간격은 일부 구간에 집중 분포되어 있다. Fig. 7은 표준화 변환 후의 히스토그램으로 데이터들의 막대그래프가 고르게 분포되었고, 물결선 또한 완만한 형태를 보여주고 있다. Fig. 8과 Fig. 9은 데이터들의 분포를 박스 플롯으로 나타내고 있다. 표준화 변환 전에는 데이터들이 각자의 영역에 분포하고 있지만, 표준화 변환 후 데이터들은 고른 분포를 보였다.
Table 4는 표준화 변환 후 F1스코어를 보여준다. 표준화 변환 후 KNN 모델의 하이퍼 파라미터는 기존과 동일하였다. KNN 모델은 F1 스코어는 불안전 클래스에 대해서는 훈련 세트 0.91, 테스트 세트 0.89이며, 안전 클래스에 대해서는 예측을 진행하지 못하였다. 로지스틱 회귀 모델은 데이터 전처리 후 하이퍼 파라미터에서 학습 횟수가 10000에서 100으로 변화가 생겼고, 이로 인해, 예측에 소요되는 시간이 단축되었다. F1스코어는 불안전 클래스에 대해서는 훈련 세트와 테스트 세트 모두 0.92로 좋은 성능을 보여주었다. 안전 클래스에 대해서는 훈련 세트 0.57, 테스트 세트 0.59로 보완이 필요하다.
4. 결 론
본 연구는 기계학습 모델을 사용한 태양광 구조물의 불안전성을 예측하는 모델을 제시하였다. 국가건설기준(KDS)의 건축구조기준 설계하중(KDS 41 10 15 : 2019)과 건축물 강구조 설계기준(KDS 41 31 00 : 2019)으로 검토된 3,061개의 결과를 학습 데이터로 사용하였으며, F1스코어를 통해 모델의 성능을 확인하였다.
- (1) KNN 모델의 하이퍼 파라미터는 K=7, Euclidean, Uniform으로 탐색되었다. 불안전 클래스는 훈련 세트 0.91, 테스트 세트 0.89로 좋은 점수를 보여주었지만, 안전 클래스는 예측을 진행하지 못하였다.
- (2) 로지스틱회귀 모델의 하이퍼 파라미터는 C=10, Liblinear, 학습 횟수 100으로 탐색되었다. 불안전 클래스는 훈련 세트와 테스트 세트 모두 0.92로 좋은 성능을 보여주었다. 안전 클래스는 훈련 세트 0.57, 테스트 세트 0.59로 보완이 필요하다.
- (3) 두 모델은 비전문가가 초기 설계 시에 태양광 구조물이 불안전한지를 판단할 수 있는 기계학습 모델을 제안하였다.
- (4) 두 모델은 안전 클래스에 대한 보완이 필요하다. 안전 클래스와 불안전 클래스 데이터 수의 차이로 인한 데이터 편향이 생긴 것으로 판단된다. 데이터 세트의 추가적인 확보나 데이터 처리 방법을 통하여 모델의 성능을 높여야 한다.
- (5) 본 연구에서는 모듈의 설치 각도, 구조물의 높이, 건축물의 지붕 각도 등은 변수에서 제외되었다. 추후, 추가적인 변수들에 대한 연구가 이루어진다면, 더 넓은 범위에서 태양광 구조물의 안전성을 판단할 수 있는 대안이 될 것이다.
Acknowledgments
이 논문은 부경대학교 자율창의학술연구비(2023년)에 의하여 연구되었습니다.
References
- Kim, C. (2021) A Review of the Deployment Programs, Impact, and Barriers of Renewable Energy Policies in Korea, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Elsevier, Vol.144, 110870.
- Kang, I.S., Moon, J.W., and Park, J.C. (2017) Recent Research Trends of Artificial Intelligent Machine Learning in Architectural Field -Review of Domestic and International Journal Papers-, Journal of the Architectural Institute of Korea Structure & Construction, AIK, Vol.33, No.4, pp.63-68 (in Korean).
- Baduge, S.K., Thilakarathna, S., Perera, J.S., Arashpour, M., Sharafi, P., Teodosio, B., Shringi, A., and Mendis, P. (2022) Artificial Intelligence and Smart Vision for Building and Construction 4.0: Machine and Deep Learning Methods and Applications, Automation in Construction, Elsevier, Vol.141, 104440.
- Kim, B.I. (2012) Optimum Design of Steel Structures Using Genetic Algorithms, Journal of Korean Society of Steel Construction, KSSC, Vol.24, No.6, pp.701-710 (in Korean).
- Kim, B.I. (2015) Optimum Design for Sizing and Shape of Truss Structures Using Harmony Search and Simulated Annealing, Journal of Korean Society of Steel Construction, KSSC, Vol.27, No.2, pp.131-142 (in Korean).
- Hashemi, S.S., Sadeghi, K., Fazeli, A., and Zarei, M. (2019) Predicting the Weight of the Steel Moment-Resisting Frame Structures Using Artificial Neural Networks, International Journal of Steel Structures, KSSC, Vol.19, No.1, pp.168-180.
- Gupta, A.K., Chakroborty, S., Ghosh, S.K., and Ganguly, S. (2023) A Machine Learning Model for Multi-Class Classification of Quenched and Partitioned Steel Microstructure Type by the K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm, Computational Materials Science, Elsevier, Vol.228, 112321.
- Lee, S., Lee, Y., Lee, K., and Lee, J. (2022) Compressive Strength Prediction of CFST Columns Using Machine Learning Methods, Journal of Korean Society of Steel Construction, KSSC, Vol.34, No.2, pp.101-110 (in Korean).
- Ha, M.-G., Kwon, T.-Y., Kim, R.-H., and Ahn, J.-H. (2024) Methods of Condition Evaluation and Assessment for paint Chalking of Steel Bridge Depending on Paint Coating Deterioration, Journal of Korean Society of Steel Construction, KSSC, Vol.36, No.1, pp.13-24 (in Korean).
- Duong, T.H., Le, T.-T., and Le, M.V. (2023) Practical Machine Learning Application for Predicting Axial Capacity of Composite Concrete-Filled Steel Tube Columns Considering Effect of Cross-Sectional Shapes, International Journal of Steel Structures, KSSC, Vol.23, No.1, pp.263-278.
- Jang, A., Kim, J., Park, M.J., Ju, Y.K., and Kim, S.J. (2022) Analysis of Machine Learning for Detect Concrete Crack Depths Using Infrared Thermography Technique, Proceedings of IABSE Symposium Prague 2022, International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering, Czech, pp.758-765.
- Kim, J., Jang, A., Park, M.J., and Ju, Y.K. (2021) Comparison Analysis of Machine Learning for Concrete Crack Depths Prediction Using Thermal Image and Environmental Parameters, Journal of Korean Association for Spatial Structures, KASSS, Vol.21, No.2, pp.99-110 (in Korean).
- Jeong, S.-G., Jang, A., Park, M.J., and Ju, Y.K. (2023) Defect Evaluation Technology for Welded Parts Using Thermal Image Based on Machine Learning, Proceedings of 2023 Autumn Annual Conference of AIK, Architectural Institute of Korea, Vol.43, No.2, pp.367-368 (in Korean).
- Architectural Institute of Korea (2019) Building Structure Standards-Design Load, KDS 41 10 15 : 2019, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (in Korean).
- Architectural Institute of Korea (2019) Steel Structures Design Standard, KDS 41 30 10 : 2019, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (in Korean).
- Thai, H.-T. (2022) Machine Learning for Structural Engineering: A State-of-the-Art Review, Structures, Elsevier, Vol.38, pp.448-491.