매니퓰레이션 시스템 이동에 따른 원격・자동화 거푸집 시스템의 안전성과 사용성 분석
Copyright © 2024 by Korean Society of Steel Construction
초록
원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템은 교각의 시공단계에서 거푸집 시스템과 매니퓰레이션 시스템을 포괄하는 교각 무인화 시공 시스템이다. 매니퓰레이션 시스템은 모바일 이동체와 매니퓰레이터로 구성되어 있으며, 거푸집 시스템 상부 작업공간에서 원형 레일을 따라 이동하면서 사람을 대신하여 철근의 배치 및 이음, 바이브레이팅 작업을 수행한다. 구조물 위에서 이동하중이 작용할 때, 구조물에 진동이 발생하여 구조물의 안전성을 저하할 수 있다. 이에 따라, 매니퓰레이션 시스템이 이동하면서 발생하는 동적 효과가 전체 구조물에 미치는 영향에 대한 검증이 필요하다. 본 연구에서는 MIDAS CIVIL을 활용하여 세 개의 매니퓰레이션이 작동할 때, 이동하중에 대한 시간이력 해석을 진행하여 전체 구조물에 대한 안전성을 평가하고, 매니퓰레이션의 이동속도에 따른 취약 부재의 처짐과 레일의 기울기를 도출하여 사용성을 분석하였다. 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템은 매니퓰레이션이 이동할 때의 작업환경에 대하여 안전성과 사용성이 확보된다는 결과를 도출했다.
Abstract
The remote automated formwork system is an unmanned construction system for piers that encompasses both formwork and manipulation systems in the construction stage. The manipulation system comprises a mobile platform and a manipulator, which move along circular rails within the upper workspace of the formwork system, performing works such as rebar placement, splicing, and vibrating work in place of human labor. When a moving load is applied to the structure, vibrations may occur, potentially undermining structural safety. Therefore, it is essential to verify the dynamic effects of the manipulation system’s movement on the entire structure. In this study time history analysis of moving loads was conducted using MIDAS CIVIL to assess the structural safety when three manipulation systems are in operation, and additionally deflection of vulnerable components and rail inclination were derived based on the manipulator’s velocity to analyze serviceability. As the result, the remote and automated formwork system ensures both stability and serviceability in the working environment when the manipulation system moves.
Keywords:
Automated construction, Steel structure, Dynamic analysis, Time history analysis, Structural safety, MIDAS CIVIL키워드:
건설 자동화, 강구조물, 동해석, 시간이력 해석, 구조적 안전성1. 서 론
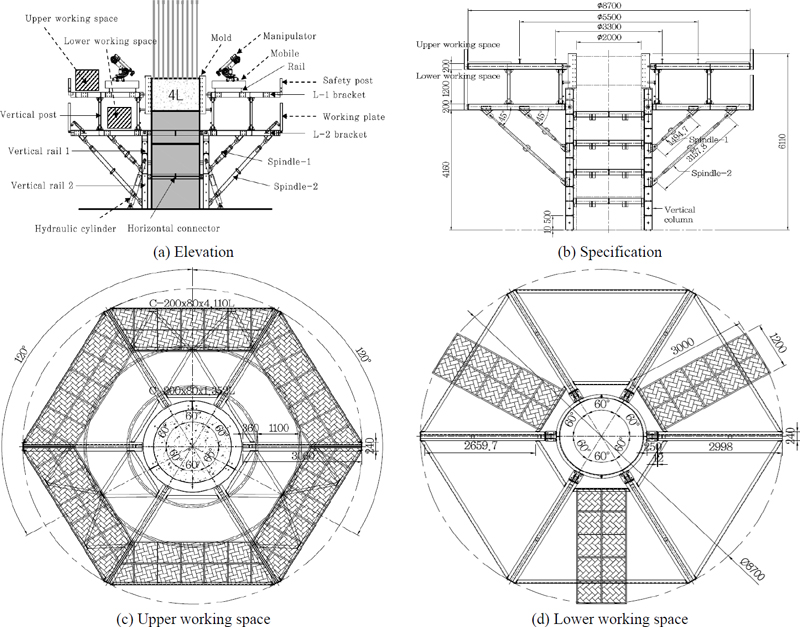
원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템(Remote Automated Formwork System)은 교각의 시공단계에서 거푸집 시스템과 매니퓰레이션 시스템(Manipulation System)을 포괄하는 교각 무인화 시공 시스템이다[1]-[3]. Fig. 1은 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템의 전체적인 형상을 보여준다. 상부 작업공간에서 원형 레일을 따라 이동하는 매니퓰레이션 시스템은 모바일 이동체와 매니퓰레이터로 구성되어 있으며, 사람을 대신하여 철근의 배치 및 이음, 바이브레이팅 작업을 수행한다. 임시적으로 운행되는 AI 기술을 접목한 계측, 시공 등의 정밀한 기계장치를 교각 시공 완료 시 재활용하기 위해 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템은 조립 및 해체가 용이한 강재로 이루어진다. 이에 따라 안전성에 대한 검증이 필요하고 정밀한 기계장치의 운용을 위하여 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템은 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 작동 기준에 적합하게 사용성 또한 확보되어야 한다.
원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템에는 매니퓰레이션 시스템을 위한 장치와 같은 고정하중과 유지보수를 위한 작업자 등 다양한 활하중이 작용하게 된다. 이에 따라, Choi et al.은 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템에 작용하는 하중을 고려한 유한요소해석을 통해 정적 하중에 대한 구조적 안전성 분석하였다[4]. 유한요소해석을 통해 구조물의 전체적인 안전성에 대하여 분석하였으며, 구조 부재의 안전성에 대한 검증이 이루어졌다. 하지만, 매니퓰레이션 시스템이 작동할 때, 구조물의 응답에 대한 검증이 필요하다.
원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템 상부에 설치되는 3대의 매니퓰레이터는 전체 연직하중의 가장 큰 비중을 차지한다. Choi et al.은 MIDAS CIVIL[5]을 이용한 곡선보에서 동해석 결과의 신뢰성에 대하여 검증하였다[6]. 검증을 위해 유한요소 모델 해석의 처짐과 Yang et al.이 유도한 이동하중이 작용하는 곡선보의 이론적 해[7]의 처짐을 비교하였다. 이론적 해와 비교, 검증을 통해 MIDAS CIVIL을 이용한 유한요소 모델은 곡선보 위의 이동하중에 대한 동적 효과를 충분히 나타낼 수 있음을 확인하였다. MIDAS CIVIL에서 곡선보를 구현화 하기 위하여 매니퓰레이션 시스템이 이동하는 일정한 곡률의 원형 곡선보 레일은 직선보 요소로 분할하여 모델링하였다.
본 연구에서는 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템 전체 모델에 대하여 상부 작업공간에서 매니퓰레이션 시스템이 곡선 레일보 위를 움직이는 상황에 대한 구조해석을 진행하고자 한다. 3대의 모바일 매니퓰레이션 시스템이 모두 작동할 때, 동해석을 통하여 전체 구조물에 대한 안전성을 평가하고, 시간에 따른 취약부의 처짐과 레일의 경사를 도출하여 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템의 작업환경을 위한 사용성을 분석하였다.
2. 원격∙자동화 거푸집 시스템
2.1 원격∙자동화 거푸집 시스템 구조 형상
Fig. 1은 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템의 구조 형상을 나타내며, 1회 콘크리트 타설 단위 4 lot(1 lot = 1 m)에 대한 구조 형상이다. 해당 구조물은 상부로 갈수록 확장되는 형태로서 최상단의 진동에 취약한 구조이다. 추후, 본 거푸집 시스템은 높이 10 m‒15 m, 직경 2 m의 원형 교각 시공을 목적으로 한다. 다음 거푸집 시스템에 대한 구조 부재의 제원은 Choi et al.[4]에 상세하게 나타나 있다.
2.2 원격∙자동화 거푸집 시스템 유한요소 모델
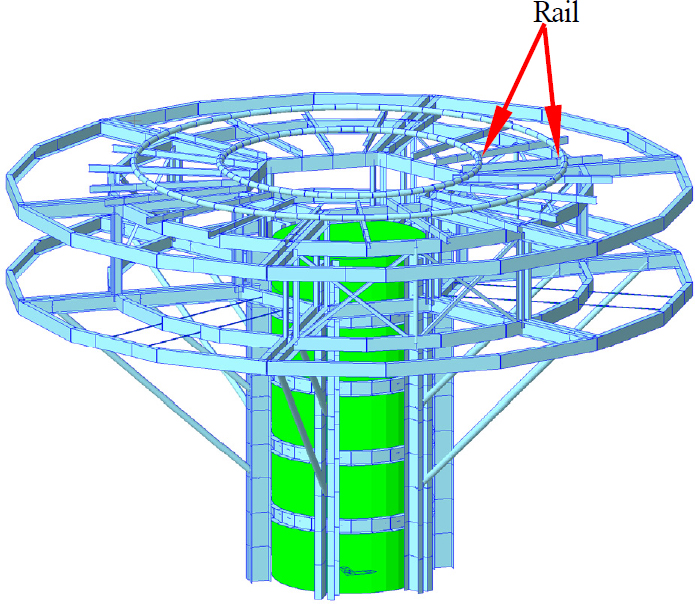
MIDAS CIVIL을 사용하여 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템의 유한요소 모델을 모델링하였다. Fig. 2는 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템의 유한요소 모델을 보여준다. 각 부재는 beam 요소로 모델링하였다. Spindle 부재의 경우 양단을 beam and release 기능을 활용하여 truss 요소와 같이 거동하게 모델링하였다. 거푸집 시스템의 중심에 있는 원기둥 기둥은 콘크리트 양생이 완료된 원형 교각이며, 외측 철골은 거푸집 시스템이다. 거푸집 시스템의 고정하중(자중)과 매니퓰레이션 시스템에 대한 사용하중, 매니퓰레이션이 출발하고 정지할 때 발생하는 시제동하중을 하중조건으로 적용하였다.
2.3 매니퓰레이션 시스템 형상
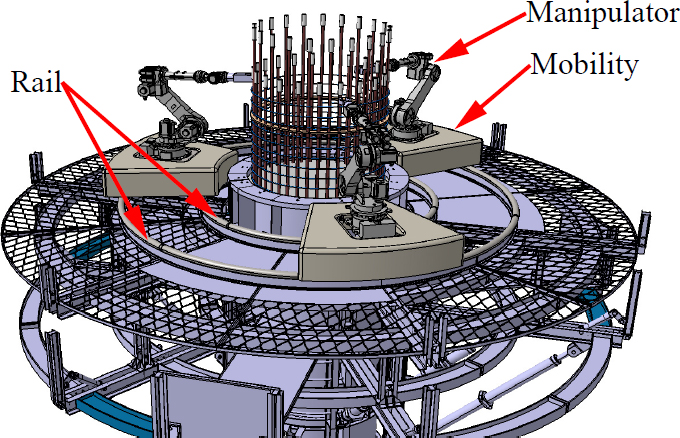
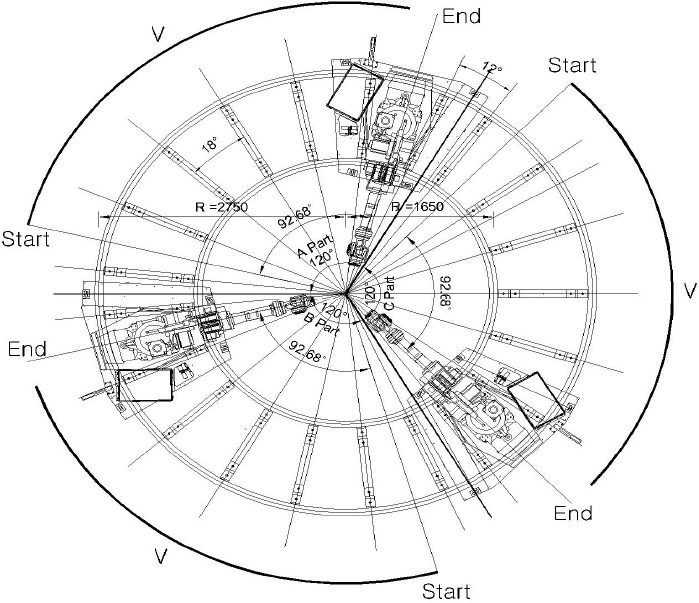
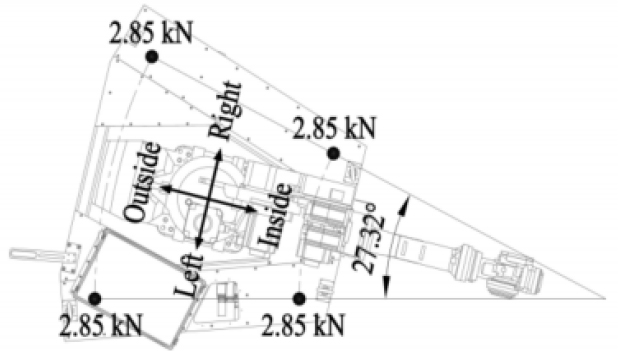
Fig. 3는 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템 위에서 교각의 주철근을 연결하는 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 모습을 보여준다. 거푸집 시스템 상부의 매니퓰레이션 시스템에 대한 작업영역과 원형 레일의 형상을 Fig. 4에 나타내었다. 3대의 매니퓰레이션 시스템은 각각 A, B, C part로 나누어진 작업영역 내에서 이동하며 작업을 진행한다. 레일 부재는 원형 파이프로 이루어져 있으며, 내곽 레일의 반지름은 1.65 m, 외곽 레일의 반지름은 2.75 m이다. 레일은 각 part 양 끝단에서 6° 떨어진 지점부터 18° 간격으로 하부(rail support)에 지지되어 있다. 각 매니퓰레이션은 각 part에서 레일을 따라 최대 92.68°를 회전할 수 있다.
2.4 매니퓰레이션 시스템 이동하중
Fig. 5에서는 하나의 매니퓰레이션에 부착된 바퀴의 위치에서 작용하는 하중의 크기를 원형 레일의 내곽 레일과 외곽 레일에 나타내었다. 1개의 매니퓰레이션 시스템 총 무게는 11.4 kN이며, 4개의 바퀴에 동등하게 하중이 분배되어 각 바퀴에 2.85 kN이 작용한다고 가정하였다. 이 매니퓰레이션 시스템은 각 part에서 v의 속도로 이동 후 정지한다고 가정한다.
레일은 일정한 곡률을 갖는 원형 곡선보이므로 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 하중은 전단력, 모멘트, 그리고 비틀림을 유발한다.
Choi et al.[6]에서는 이동하중이 작용하는 곡선보에서 MIDAS CIVIL을 이용한 동해석 기법을 제시하는데, 유한요소 모델에서 하중에 대하여 곡률 효과를 고려한 하중 분배를 적용할 때 Yang et al.[7]에서 제시한 곡선보의 이론해와 유사한 곡선보의 동적 응답이 나타난 것을 확인하였다.
이에 따라, MIDAS CIVIL에 하중조건을 적용할 때, 이동하중에 대한 동적 효과를 충분히 나타낼 수 있도록 곡률 효과를 고려한 하중 분배를 적용하였다.
3. 원격∙자동화 거푸집 시스템의 안전성
3.1 해석 개요
매니퓰레이션 시스템이 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템 상부 작업공간에서 이동함에 따라 발생하는 동적 효과를 고려한 부재력 검토를 진행하였다.
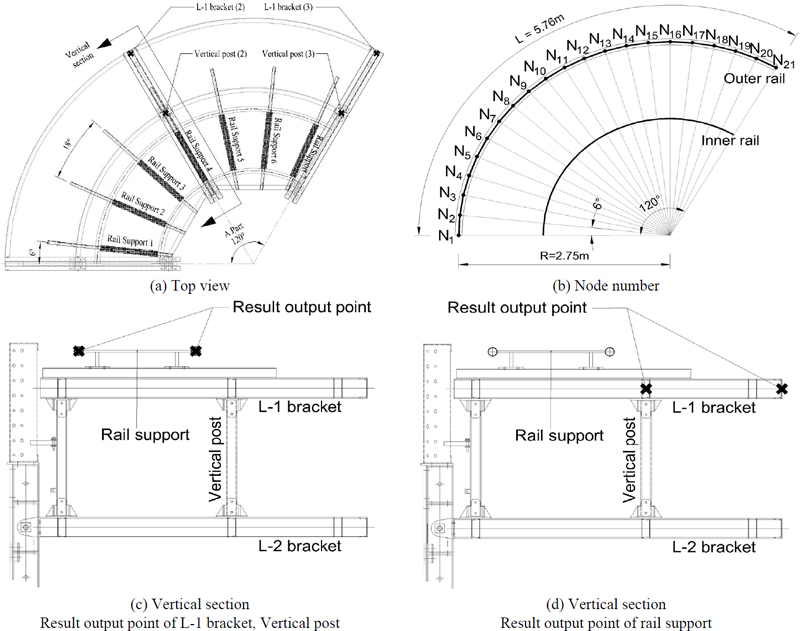
정적해석 하에 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템 부재의 안전성은 한계상태설계법을 사용하여 검토하였고, 하중조합은 교량설계하중 KDS 24 12 11 : 2021[9]에서 제시한 (1.0DC + 1.3LL)을 적용하였다. 매니퓰레이션이 이동함에 따라, 매니퓰레이션이 곡선 레일보를 따라 Fig. 6(b)의 17개의 Node(N3 ‒ N19)에 위치할 때 정적해석을 진행하여 최대 부재력을 산정하였다.
동해석 하에 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템 부재의 안전성은 동적 효과를 나타내기 위하여 (1.0DC + 1.0DY)의 하중조합을 사용하였고, DY는 동적 하중이다. MIDAS CIVIL의 시간이력 해석을 통하여 매니퓰레이션이 속도 v = 1 m/s로 이동할 때 부재력을 검토하였다. 매니퓰레이션이 속도 v = 1 m/s로 이동한다면 시작 지점부터 끝나는 지점까지 5.76초가 소요된다. 이 시간의 간격을 0.01초로 설정하여 시간이력 해석을 진행하였다.
수직 요소로 이루어진 부재(Main Post, Vertical Post, Spindle, Bracing)는 축력에 대한 검토를 진행하였고, 수평 요소로 이루어진 부재(L-1 bracket, L-2 bracket, Inner beam, Horizontal beam, Handrail beam, Rail)에 대해서는 휨모멘트에 대한 검토를 진행하였다.
3.2 해석 결과
곡률 효과를 고려한 동적 하중에 대한 효과를 확인하기 위하여 정적 하중(자중)에 의해 발생하는 최대 부재력을 따로 표시하였다(1.0DC). 정적 하중 및 활하중에 대한 정적해석(1.0DC + 1.3LL), 정적 하중 및 동적 하중에 대한 동해석(1.0DC + 1.3DY)을 통하여 도출한 부재력은 Table 1에 나타내었다.
정적 하중을 제외한 활하중에 대한 정적해석 결과에 안전계수를 곱한 값(1.3LL)과 동적 하중에 대한 동해석 결과(1.0DY)를 비교하였을 때, L-1 Bracket과 Rail 부재에서 유사한 값이 도출되었다. 매니퓰레이션이 이동할 때, L-1 Bracket과 Rail 부재에서 동적 효과가 발생한다는 것을 확인하였다.
안전성 검토 결과, 부재에서 발생하는 최대 부재력은 각 부재의 공칭 저항 강도를 초과하지 않는 것으로 확인되었으며, 정적해석, 동해석 결과 각 부재의 최대 부재력은 각 부재의 공칭 저항 강도 대비 2.7 %‒31.0 %로 충분한 안전성을 확보하는 것으로 확인되었다.
4. 원격∙자동화 거푸집 시스템의 사용성
4.1 해석 개요
원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템에서 매니퓰레이션이 레일 위를 이동할 때 직접적으로 지지하는 주요 부재(L-1 bracket, Vertical post)의 거동을 파악하여 부재의 사용성을 확인하였다. 동해석을 진행할 때 매니퓰레이션의 이동속도 v를 1 m/s, 5 m/s로 설정하고, 매니퓰레이션이 이동함에 따라 발생하는 하중을 시간에 따른 이동하중으로 적용하였다. 매니퓰레이션의 이동하중의 각속도(w=v/R)에 따라 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 한 개의 요소 길이 l(분할된 직선 요소의 길이)을 통과하는데 소요되는 시간은 (6°/w)초가 필요하다. 전체 작업공간을 이동하는 경우, 이동속도 v = 1 m/s일 때는 5.76초 동안 이동하며, v = 5 m/s일 때는 1.78초 동안 이동한다. 이에 따라 시간의 간격을 0.01초로 설정하여 시간이력 해석을 수행하였다. 시간이력 해석을 통해 레일을 직접적으로 지지하는 주요 부재의 거동을 파악하여 정적해석 결과와 비교하였다. 구조물의 감쇠율은 교량 내진설계기준 KDS 24 17 10 : 2018[10]에서 제시한 감쇠비를 기준으로 보다 안전한 검토를 하기 위하여 2 %로 가정하였다. 또한 외곽 레일과 내곽 레일의 지점 변위차를 확인하여 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 작업환경을 위한 사용성을 분석하였다.
Fig. 6(a)에서는 구조해석을 진행할 작업영역 A part의 L-1 bracket(2), L-1 bracket(3), Vertical post(2), Vertical Post(3), rail support의 평면도와 해석 결과 도출 지점을 나타내었다. Fig. 6(b)에서는 각각의 beam 요소로 모델링한 곡선보를 보여주며, 각 요소의 길이는 외곽 레일에서 약 288 mm, 내곽 레일에서 약 173 mm이다. 이러한 요소의 크기는 원형 레일의 효과를 충분히 나타낸다. 매니퓰레이션이 이동함에 따라 위치를 특정하기 위하여 외곽 레일을 따라 움직이는 매니퓰레이션의 두 바퀴 중심의 위치를 절점 번호(Node Number)로 나타내었다.
Fig. 6(c)에서는 L-1 Bracket, Vertical post의 해석 결과 도출 지점을 나타내었다. Fig. 6(d)에서 7개의 Rail support의 해석 결과 도출 지점을 나타내었다.
4.2 해석 결과
Fig. 7과 Fig. 8에서는 정적해석과 이동속도가 1 m/s, 5 m/s일 때의 동해석 결과를 비교하여 보여준다. 그래프의 x축은 절점 번호(Node number)에 따라 나타내었다.
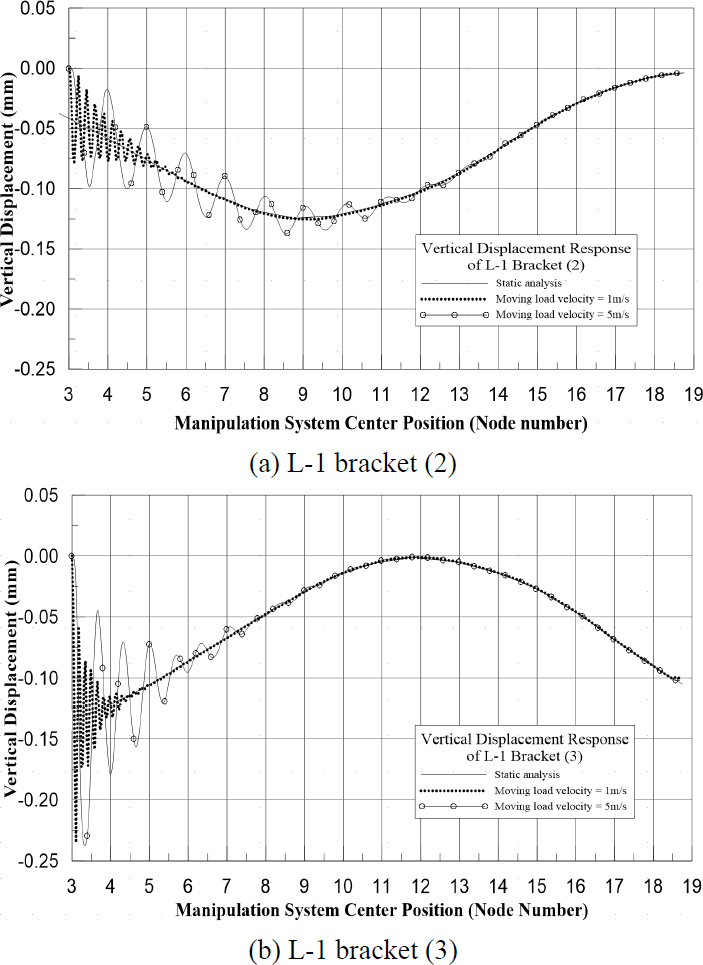
Fig. 7은 L-1 Bracket 부재 외곽 지점에서의 수직 응답을 보여준다. Fig. 7(a)에서 L-1 Bracket (2)의 수직 응답은 매니퓰레이션의 이동속도가 1 m/s일 때 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 Node 6를 통과한 이후, 이동속도가 5 m/s일 때 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 Node 13을 통과한 이후 정적해석과 유사한 거동을 보여준다. Fig. 7(b)에서 L-2Bracket (3) 부재의 수직 응답은 매니퓰레이션의 이동 속도가 1 m/s일 때 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 Node 5를 통과한 이후, 이동속도가 5 m/s일 때 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 Node 9를 통과한 이후 정적해석과 유사한 거동을 보여준다.
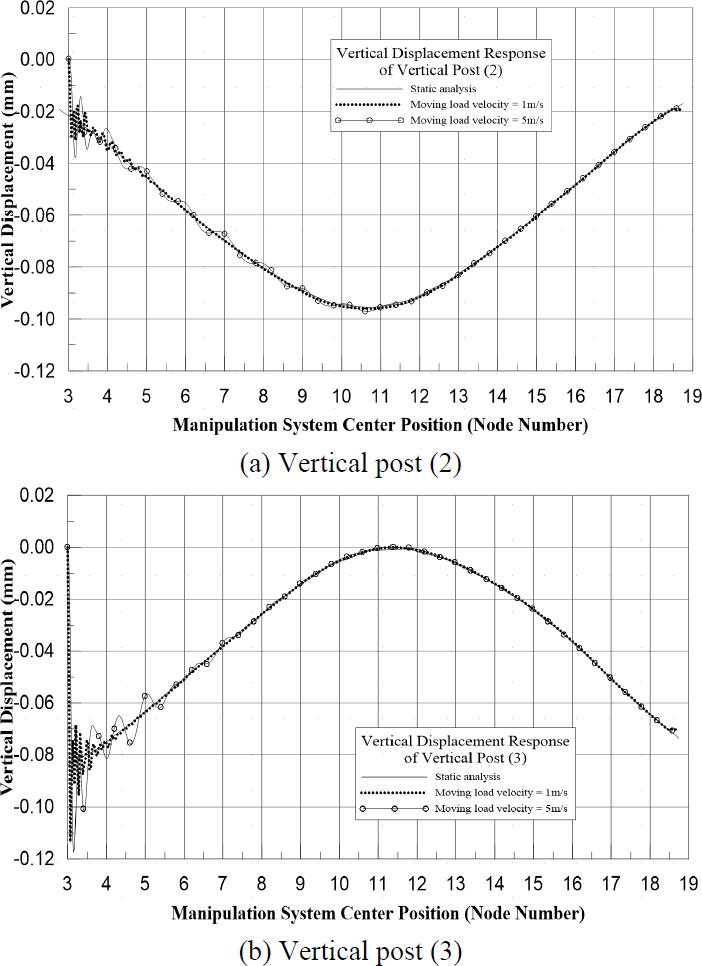
Fig. 8은 Vertical Post 부재에서의 수직 응답을 보여준다. Fig. 8(a)에서 Vertical Post(2)의 수직 응답은 매니퓰레이션의 이동속도가 1 m/s일 때 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 Node 6을 통과한 이후, 이동속도가 5 m/s일 때 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 Node 13을 통과한 이후 정적해석과 유사한 거동을 보여준다. Fig. 8(b)에서 Vertical Post(3)의 수직 응답은 매니퓰레이션의 이동속도가 1 m/s일 때 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 Node 5를 통과한 이후, 이동속도가 5 m/s일 때 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 Node 9를 통과한 이후 정적해석과 유사한 거동을 보여준다.
이동속도가 1 m/s, 5 m/s일 때 동해석에 대한 수직 응답을 정적해석 결과와 비교하였을 때, 매니퓰레이션 시스템이 각 작업영역의 절반 이상 진행하였을 경우 동적 효과는 미미해지는 것으로 확인되었다.
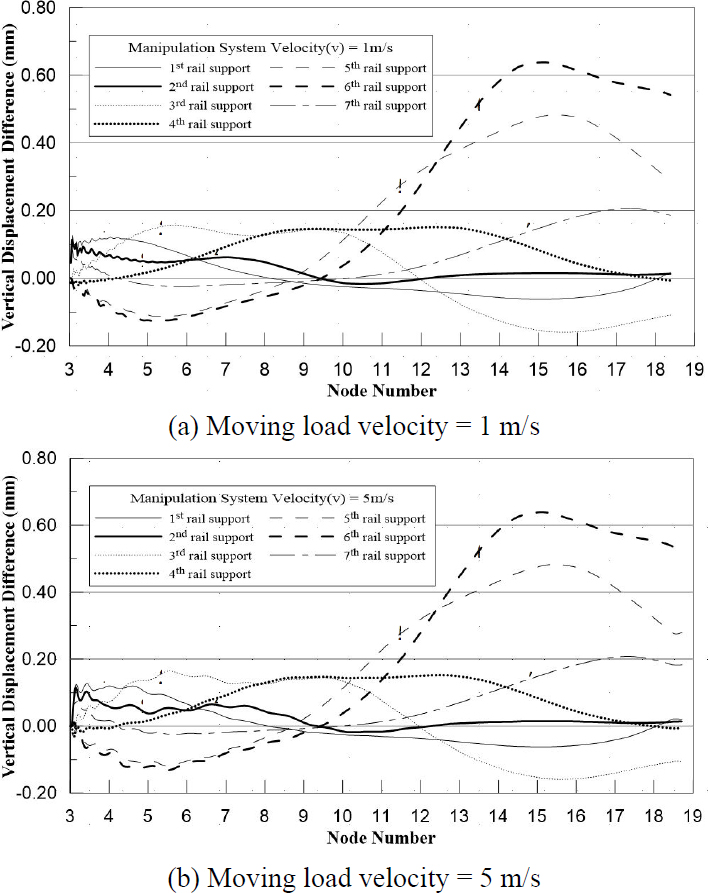
Fig. 6(a)에서 7개의 Rail Support 부재에 대하여 Fig. 6(d)에서 나타낸 Rail Support 두 지점에서의 처짐차이를 유한요소해석을 통해 도출했다.
Fig. 9(a)와 Fig. 9(b)는 각각 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 이동속도가 1 m/s, 5 m/s일 때, 레일 두 지점 사이에 발생한 처짐 차이(외곽 레일 처짐-내곽 레일 처짐)를 보여준다. x축은 절점 번호(외곽 레일을 따라 움직이는 두 바퀴의 중심)에 따라 나타내었다. 이동속도 v = 1 m/s일 때, 최대 변위차는 0.68 mm이고, 이동속도 v = 5 m/s일 때, 최대 변위차는 0.69 mm이다. 또한, 두 그래프는 비슷한 양상을 보이는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 레일 두 지점 사이의 경간(1.1 m)을 고려하였을 때, 최대 경사는 0.06 %이다.
5. 결 론
본 연구에서는 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템에 대한 안전성을 평가하기 위하여 매니퓰레이션의 이동속도를 1 m/s로 설정하여 시간이력 해석을 수행하였다. 이를 정적해석 결과와 비교하여 부재력을 검토하였다. 또한 매니퓰레이션이 이동하는 상황에 대한 사용성을 검토하기 위하여 매니퓰레이션의 속도를 1 m/s, 5 m/s로 설정하여 시간이력 해석을 수행하였고, 정적해석 결과와 비교하여 부재의 변위차를 도출하였다.
- (1) 매니퓰레이션이 이동하는 상황에 대하여 정적해석, 동해석 하 부재력 검토를 진행하였을 때, 모든 부재는 각 부재의 공칭 저항 강도를 초과하지 않는 것을 확인하였다.
- (2) 매니퓰레이션의 이동속도에 따른 수직 응답을 비교하였을 때, 매니퓰레이션 시스템의 중심이 곡선보의 절반 이상 이동하면 정적해석과 동해석의 해석 결과가 유사해진다. 이를 통해 매니퓰레이션이 작업영역에서 절반 이상 이동하면 동적 효과가 미미하다는 것을 확인하였다.
- (3) 매니퓰레이션이 이동함에 따라 발생하는 외곽 레일과 내곽 레일 두 지점 사이의 최대 변위차는 이동속도가 5 m/s일 때 0.69 mm이고, 두 지점 사이의 경간(1.1 m)을 고려하였을 때 최대 경사는 0.06 %이다.
이에 따라, 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템은 매니퓰레이션이 움직이는 상황에 대해 구조적 안전성이 확보된다. 또한, 현재 제작 중인 원격·자동화 거푸집 시스템 위 매니퓰레이션은 rail support가 0.06 % 기울어진 환경에서도 작업이 가능하며, 사용성이 충분히 확보되는 것으로 확인된다.
Acknowledgments
본 연구는 국토교통부/국토교통과학기술진흥원이 시행하고 한국도로공사가 총괄하는 “스마트건설기술개발 국가 R&D 사업(RS-2020-KA157074)”의 지원으로 수행되었습니다. 이에 감사드립니다.
References
- Shim, C., Lee, S., and Sim, S. (2020) Smart Construction Technologies for Roadway Structures, The Magazine of the Korean Society of Civil Engineers, KSCE, Vol.68, No.8, pp.36–43 (in Korean).
- Lee, S. (2021) Development and Application of Robotic Construction, The Magazine of the Korean Society of Civil Engineers, KSCE, Vol.69, No.4, pp.34–42 (in Korean).
- Choi, D.H., Yoon, H.J., Lee, H.J., Lee, J.H., Shim, S.H., and Kim, S.H. (2024) An Analysis of Structural Behaviors of Unmanned Smart Form System for Piers to Moving Loads, Proceedings of Annual Conference of Korean Society of Steel Construction, KSSC, pp.29–30 (in Korean)
- Choi, D.-H., Lee, S.H., and Lee, H.J. (2022) Structural Safety of Unmanned Smart Form System for Piers, Journal of Korean Society of Steel Construction, KSSC, Vol.34, No.6, pp.411–418 (in Korean).
- MIDAS Information Technology (2023) Civil 2023 v1.1, MIDAS IT (in Korean).
- Choi, D.-H., Lee, H.J., and Ma, C.Y. (2023) Dynamic Analysis of Curved Beams with Moving Load Using MIDAS, Journal of Korean Society of Steel Construction, KSSC, Vol.35, No.6, pp.417–425 (in Korean).
- Yang, Y.-B., Wu, C.-M., and Yau, J.-D. (2001) Dynamic Response of a Horizontally Curved Beam Subjected to Vertical and Horizontal Moving Loads, Journal of Sound and Vibration, Elsevier, Vol.242, No.3, pp.519–537.
- Lee, S. (2021) Development of Remote and Automated Construction Technologies for Road Structure, Stage Report, Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (in Korean).
- Korean Institute of Bridge and Structural Engineers (2021) Bridge Design Standard, KDS 24 12 11 : 2021, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (in Korean).
- Korea Rail Network Authority (2018) Bridge Design Standard, KDS 24 17 10 : 2018, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (in Korean).